Data structures are essential in the fields of programming and computer science for effectively organizing and manipulating data. They act as the building blocks for managing and storing data in a form that makes it simple to access, retrieve, and modify. The three basic data structures of lists, tuples, and dictionaries will all be covered in this article, along with how to access and work with the data they hold. Additionally, we will learn about the power of list comprehensions, a clear and effective tool for more beautiful and effective list creation.
Understanding Lists
Creating Lists
By putting a comma-separated list of values in square brackets will produce a list. For Example:
Accessing and Modifying List Items
We use indexing to get access to certain elements within a list. The first item is at index 0, the second at index 1, and so on since Python utilizes a zero-based indexing system. For example:
Working with Tuples
Tuples are another way to store groups of elements that are similar to lists. Tuples, however, cannot have their elements modified after they are created because they are immutable. '()' parentheses or no delimiters are used to define more than one. Let's examine tuples in more detail:
Diving into Dictionaries
Creating Dictionaries
The definitions from the dictionary are enclosed in curly brackets, "{}" A colon separates each key-value pair, and commas divide the pairs. Here's an example:
Accessing and Modifying Dictionary Items
To access a value in a dictionary, we use the associated key:
Dictionaries are mutable, so you can change the value associated with a key:
Unleashing List Comprehensions
Python's list comprehensions are a simple yet stylish approach to build lists. They offer an easy syntax for producing lists from already-existing iterables like lists or tuples. In comparison to conventional for loops, list comprehensions are not only easier to learn but also more effective. Let's explore list comprehensions' magic:
Creating Lists with List Comprehensions
Suppose we want to create a list of the squares of numbers from 1 to 5 using a traditional for loop:
The same result can be achieved with a list comprehension in a single line:
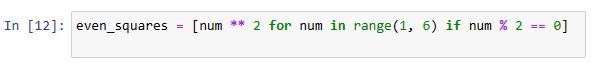
List comprehensions can also include conditions:
Conclusion
We've gone through three important Python data structures in this article: lists, tuples, and dictionaries. In order to efficiently organize information, we have learnt how to build, access, and modify data within these structures. We've also discovered the beautiful simplicity of list comprehensions, an easy method for producing lists with amazing efficiency.
A solid understanding of these data structures will be very useful as you continue your programming efforts. In order to become a skilled programmer, learning data structures is an essential first step. This is true whether you're working with huge datasets, creating complex algorithms, or simply optimizing your code. So make your coding journey succeed by exploring the world of lists, tuples, dictionaries, and list comprehensions.
Coding is fun!
.png)